Comet Multi-Plate Radiation Shield for Weather Sensors
✔FREE Domestic Shipping Orders $99+
✔Live Expert Customer Service
✔Best Price Guarantee
✔Easy 30-Day Returns
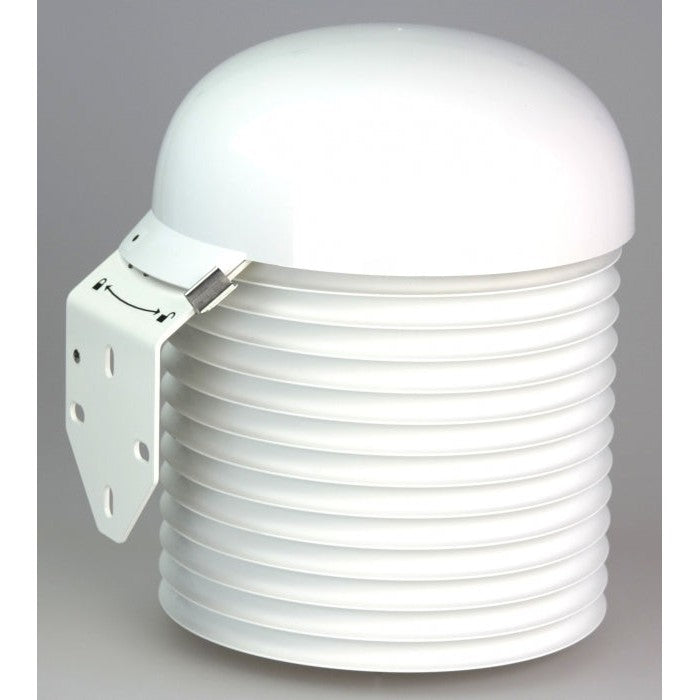
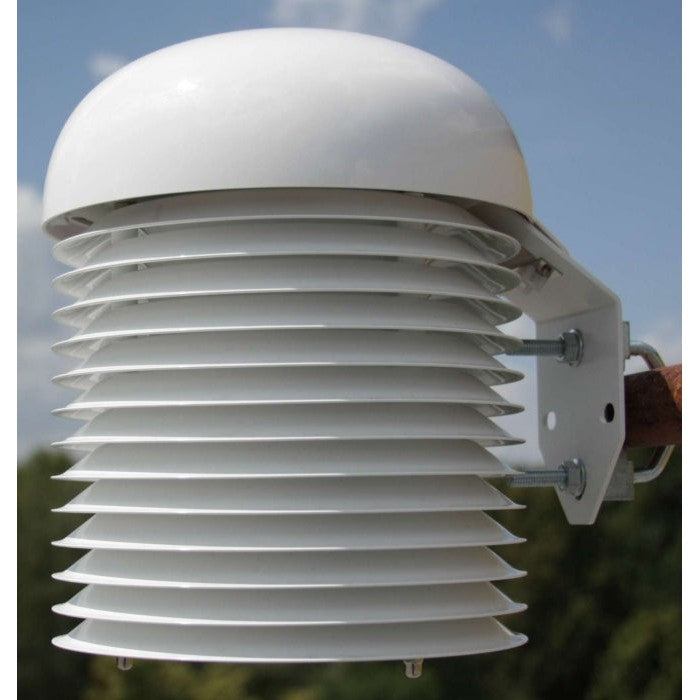
Comet Multi-Plate Radiation Shield for Weather Sensors
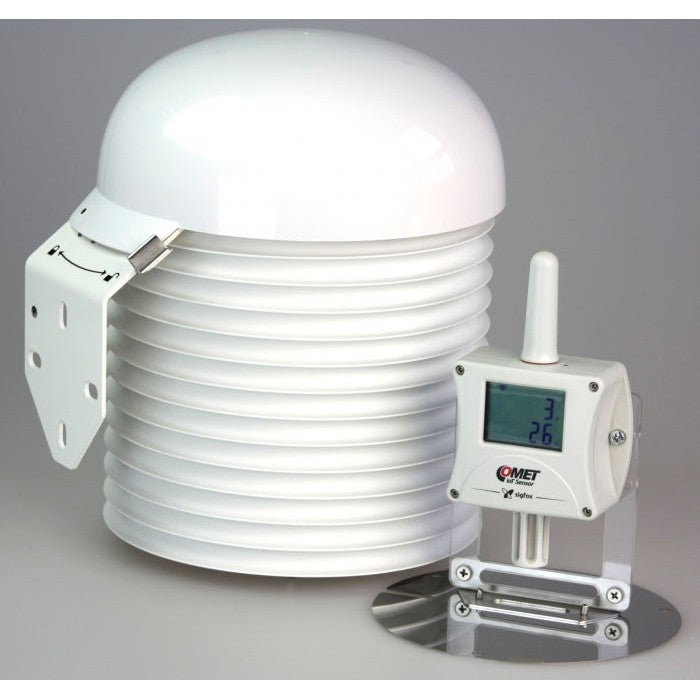
Passive solar radiation shield for better protection of weather sensors and barometers and for more accurate measurement, naturally ventilated.
"Not only radiation shield, but the complete COMETEO system minimizing negative effects"
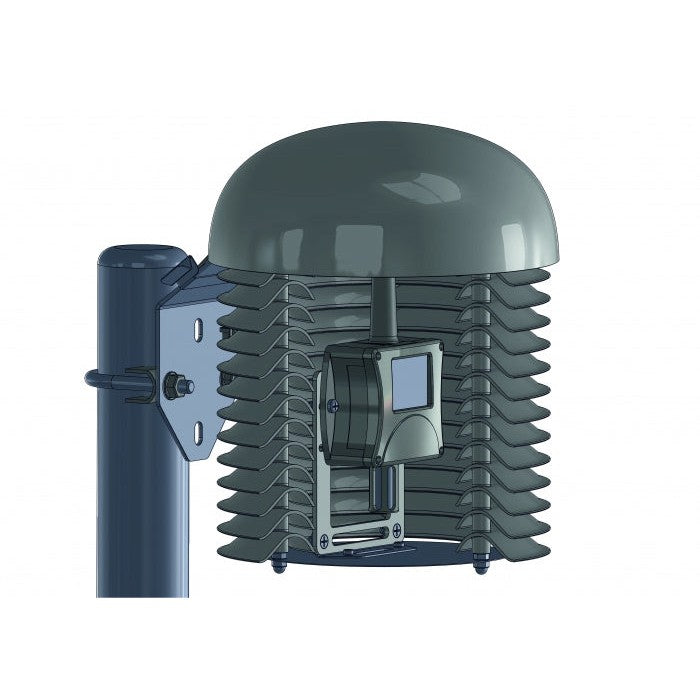
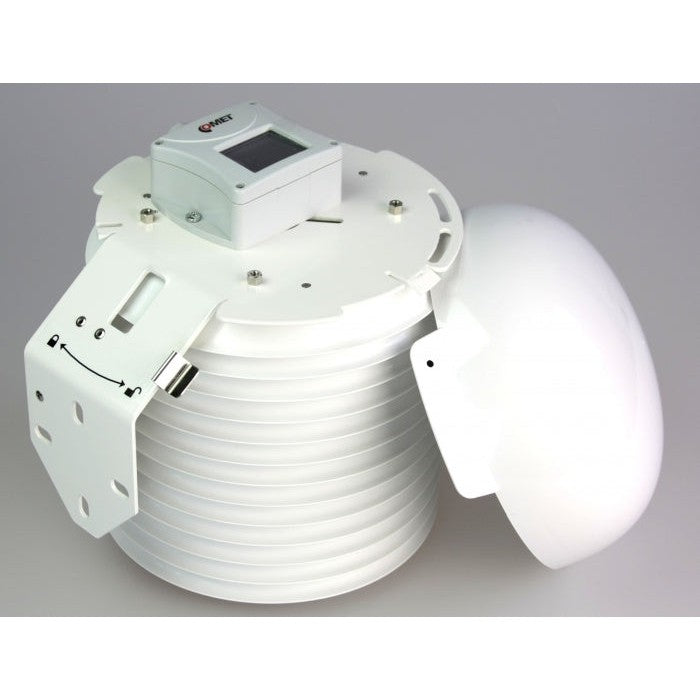
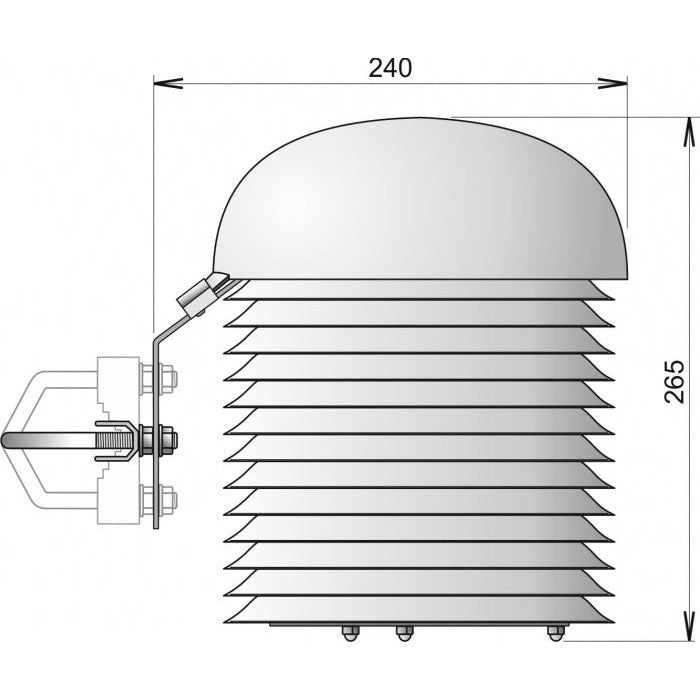
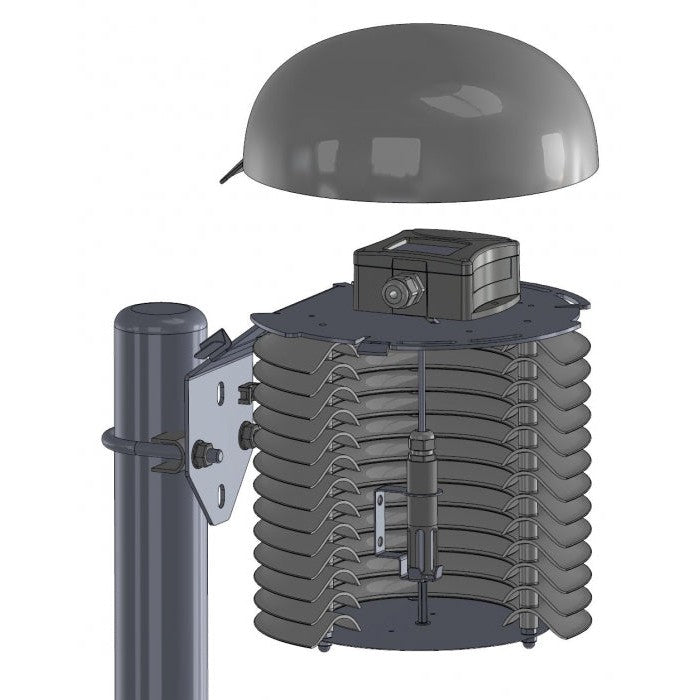
Multiplate radiation shield is used to protect measuring devices and provides more accurate measurement results. The shield minimizes radiation reaching the sensor, minimizes radiation absorbed by the shield and maximizes ambient air flow around the sensor. The enlarged 200mm diameter of 13 plates is designed to provide full protection of measuring device. Cylindrical space with 110mm diameter and 185mm height is available inside of plates for the installation of measuring device with minimized solar radiation.
Excellent wasp and bug deterrence.
TECHNICAL DATA
MEASURED VALUE
- Temperature
- Relative humidity
- CO2
- Atmospheric pressure
GENERAL TECHNICAL DATA
- Temperature operating range -40 to +80 °C
- Relative humidity operating range 0 to 100 %RH
- Storage temperature range -40 to +80 °C
- Storage relative humidity range 0 to 100 %RH (no condensation)
- Dimension 220 mm (diameter), 250 mm (height)
- Weight approx. 900 g
- Material ASA - UV stabilized, antistatic
- Warranty 3 years
FEATURES
COMETEO is made of ASA plastic which is resistant to mechanical damage and UV radiation. ASA plastic is very stable over time. Transmitter is entirely protected inside the radiation shield by maximized diameter of plates providing advanced weather protection.

AIR TEMPERATURE IN METEOROLOGY
The measurement of air temperature in meteorology is a difficult task. Accurate air temperature measurements require minimization of local effects (e.g. trees and buildings) and minimization of environmental effects that influence the actual sensing of the temperature at the position of the sensor. World Meteorological Organization - WMO defines internationally the temperature of the air nearby the earth's surface as “the temperature indicated by a thermometer exposed to the air in a place sheltered from direct solar radiation” (WMO, 1992).
The main functions of thermometer shields are to protect the sensor from direct or indirect radiation from the sun during the day and from radiation from the sensor to the sky at night and to protect the sensor from wetting. Wetting of the sensor and screen is caused by fog, drizzle or rain. But protection against radiation and wetting conflicts with the requirement of sufficient ventilation. Due to insufficient ventilation a microclimate develops within the screen. In fact, all screens develop their own microclimate and the difference with the ambient climate depends on screen type and design. It may be stated that the larger the bulk of a screen, the stronger the microclimate within the screen and the more the sensed temperature deviates from the real air temperature. From the above, it follows that thermometer screens should have a high reflectivity to minimize heating of the plates and subsequent warming of the air as it flows over the plates to the sensor. To decrease the time the air is in contact with the plate, the plate radial distance should be as small as possible. To prevent the development of microclimates within screens, also the blockage of ambient airflow by the screen should be minimized by making the plate spacing as large as possible, taking into account the requirement that wetting of the sensor should be prevented. Any design of a thermometer screen is a result of compromises. Finding the optimal design is a serious challenge that may require the use of different methods for studying the behavior of screens. In the field, the actual differences between the air temperature in the screens and the ambient air temperature depend mainly on the prevailing weather conditions. Furthermore, the state of the ground and humidity of the soil will also affect the air temperature in the screen as radiation or reflection will cause screen dependent biases. This can easily occur in areas with snow cover and in deserts.
Manuals